In Summary
The Electrical Instrumentation craftsperson is involved in the installation, commissioning, testing, and maintenance of various wiring systems and services within the commercial and industrial sector.
Their work also includes the maintenance and repair of all instruments used in the measurement and control of process variables (e.g. in the chemical industry to measure and control the temperature, pressure, and flow, as appropriate, in various points of the process).
An Electrical Instrumentation craftsperson installs, maintains, and calibrates instruments, sensors, and control systems used to measure, monitor, and protect physical quantities in industrial settings.
Measuring and controlling these quantities ensures that products are manufactured to specification while maintaining the safety of personnel, equipment, and the environment.
Electrical Instrumentation craftspersons work in the installation and maintenance of measurement and control systems across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food production, and more.
Click on the image above to view the Electrical Instrumentation brochure.
View Occupation Profile from Apprenticeship.ie
To view full details of this occupation, view information from our Careers database for the following occupation: Electrical Instrumentation
Entry Requirements
The minimum age at which the employment of an apprentice may commence is 16 years of age.
The minimum educational requirements are:
Grade D or "Achieved" in five subjects in the Department of Education & Skills Junior Certificate Examination or an approved equivalent,
or
The successful completion of an approved Pre-Apprenticeship course,
or
Three years’ work experience gained over sixteen years of age in a relevant designated industrial activity as SOLAS shall deem acceptable.
Be employed as an apprentice in your chosen occupation. Your employer must be approved to train apprentices and must register you as an apprentice within two weeks of recruitment.
Pass a colour vision test approved by SOLAS.
To become an electrical instrumentation apprentice, you must pass the Ishihara Colour Vision Test (24 Plate Edition). For further information, contact your local Education and Training Board
Note: These are the current approved minimum educational requirements for apprenticeship programmes. Previous experience in the following subjects would be an advantage, but is not essential:
- Mathematics
- Technical Drawing/Graphics
- Technology
- Physics
Training
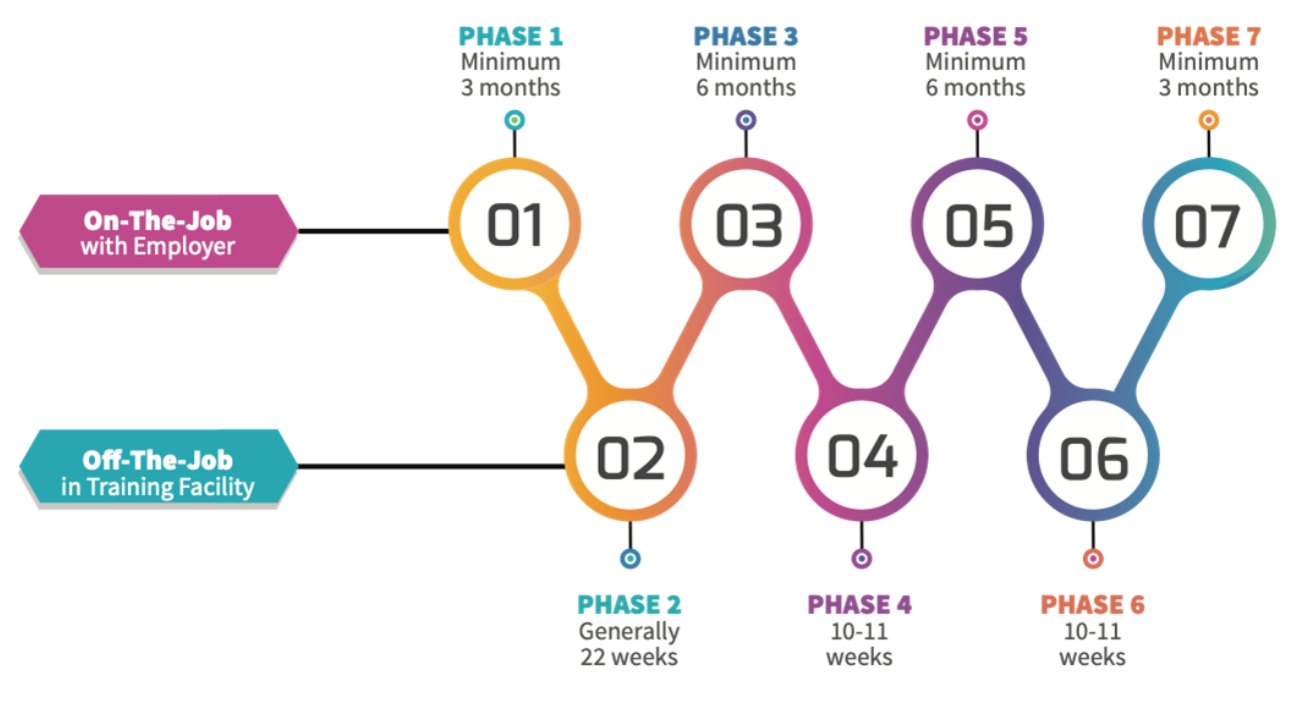
Phase 1: With Employer
- Induction Training
- Introduction to Health & Safety
- Introduction to Tools & Equipment
- Introduction to Basic Skills
Phase 2: Delivered in Training Centre (27 weeks)
Course Content:
- Induction
- Electricity/Electronics
- Installation Techniques
- Measurement - Pressure
- Measurement - Flow
- Measurement - Level
- Measurement - Temperature
- Automatic Control
- Related Theory
- Work Based Training and Assessments
Phase 4: Delivered in Educational College (21 weeks)
- Electricity, Motors & Motor Control and Power Distribution
- Hazardous Environments
- Electronics
- Measurement
- Final Control Elements
- Automatic Control
- Related Theory
- Work Based Training and Assessments
Phase 6: Delivered in Educational College (11 weeks)
- Electricity, Motor Speed Control and Measurement
- Switchboards & Switch Gear
- Electronics
- Communications Systems
- Related Theory
- Work Based Training and Assessments
A Level 6 Advanced Certificate Craft – Electrical Instrumentation is awarded to the learner on successful completion of this apprenticeship programme.
Skills & Qualities
As an Electrical Instrumentation craftsperson, you will need to be physically active and skilled at working with your hands.
A strong awareness of health and safety, good housekeeping practices, attention to detail, and an eye for aesthetics are also essential.
The Electrical Instrumentation craftsperson must have the ability to:
- Plan and organise
- Communicate effectively
- Solve problems
- Work independently and as part of a team
- Show a positive attitude
- Recognise the need for good customer relations
- Demonstrate good work practices including time keeping, tidiness, responsibility, quality awareness, and safety awareness.
Core Skills
- Selection, procurement, safe use of, and storage of craft-related tools, equipment and materials
- Selection and utilisation of fixing devices
- Assessment, interpretation and implementation of ETCI wiring regulations, installation inspection and testing procedures
- Utilisation of electrical test instruments
- Installation of steel conduit wiring systems
- Installation of plastic conduit wiring systems
- Installation of steel trunking cable systems
- Installation of plastic trunking cable systems
- Installation of cable tray and ladder systems
- Installation of industrial cable systems
- Installation of sub-distribution boards and protective devices
- Installation and maintenance of lighting, heating and motive power systems and controls
- Installation and testing of overcurrent and earth leakage protection systems
- Installation of earthing and bonding systems
- Interpretation of circuit schematics and architectural drawings which incorporate IEC symbols
- Interpretation of technical data and manufacturing standards
- Interpretation of equipment assembly, disassembly and adjustment procedures
- Completion and updating of job-related documentation
Specialist Skills
- Installation of wiring systems and equipment in hazardous environments
- Assembly and wiring of main distribution boards
- Assembly and wiring of motor control panels
- Installation of door entry/exit systems
- Installation and maintenance of emergency lighting systems
- Installation and maintenance of fire alarm systems
- Installation and maintenance of intruder alarm systems
- Installation and maintenance of standby power and battery systems
- Installation of lightning protection systems
- Installation and maintenance of MV transformers and switchgear
- Installation of metering systems
- Installation of power factor correction systems
Common Skills
- System fault analysis skills
- Interpretation of electrical/electronic schematic diagrams
- Interpretation of flow, function and ladder charts
- Soldering and desoldering skills
- Testing, removal and replacement of electronic components/PCBs
- Installation and programming of PLC systems
- Installation and calibration of sensors and transducers
- Installation of electro-pneumatic systems
- Installation of data communication cable systems
Personal Skills
- Analytical ability
- Communications
- Customer relations
- Adaptability
- Ability to work as part of a team
- Ability to work independently
- Initiative and Adaptability
- Problem solving
- Planning
- Information gathering
- Quality Assurance
- Report Writing
- Safety
Note: A person wishing to become an apprentice Electrical Instrumentation Craftsperson must pass a colour–vision test approved by SOLAS.
Work Activities
- Learning and developing new practical craft-related skills, knowledge, and competence
- Working with and learning from experienced craftspersons
- Comply with health and safety requirements
- Working with electricity or electronics
- Understanding and using physics
- Using mathematics to solve technical or scientific problems
- Being responsible for controlling or adjusting equipment
- Working on machines/processes
- Understanding technical drawings and diagrams
- Accuracy and attention to detail
- Being accurate with numbers in counting, measuring, and arithmetic
- Working with a variety of specialised hand tools, power tools, and equipment
- Keeping accurate records of all calibrations or reports
- Being well organised and careful with practical tasks
- Taking responsibility for their own learning, including the allocation of study time
- Being physically active
- Passing all your phase exams (theory, practicals skills demonstration)
- Earning as you learn
Career Progression
On successful completion of the apprenticeship programme, apprentices are qualified to work within the recognised trade or profession.
Opportunities may arise for promotion to supervisor roles. Many craftspersons use their apprenticeship qualification as a platform to pursue careers as engineers, managers, business owners, teachers, instructors, and other related professions.
For those seeking to advance, career progression options include:
- Plant Manager
- Supervisor
- Maintenance Technician / Manager
- Facilities Manager
Where apprentices and crafts persons demonstrate the necessary ability, initiative, and basic qualifications, opportunities for advancement are available. These may include advanced technological and management courses offered by technological universities, colleges of management, professional institutes, or similar organisations.
People in employment have multiple options for both educational and career Progression. Promotion within your current company may be possible.
By using your existing qualifications and experience, you may be able to secure a more senior position in another company or establish your own business.
Whatever route you choose, remember that education is a lifelong pursuit–you can always continue to upskill or retrain, whatever your age.
Links to relevant educational and enterprise supports can be found below.
Career Progression Useful Links:
Educational Supports:
On completion of an apprenticeship, your educational progression options may be offered as full awards on the National Framework of Qualifications (NFQ) Levels 7-10.
You may also decide to embark on a partial award or upskill in a particular area by undertaking a short specialised course. Depending on your skills, knowledge, and experience, some of the opportunities below may be useful to help develop your career pathway.
- Springboard & conversion courses
- Skillnet Sector learning network courses
- Skills to advance Local ETB Board
- Further education training centres FETCH Courses
- Post graduate education Search Post Graduate options
Enterprise and Self-Employment Support:
On completing the apprenticeship, if you have the appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience, you may choose to set up your own business. The links below may be useful in supporting you in this process.
- Local Enterprise Offices For profit Local enterprise support
- Local Area partnerships For profit enterprise support
- Social entrepreneurs Not-for-profit enterprise support
- Franchising Developing your business under an established franchise
Getting this Apprenticeship
To become an apprentice in Ireland, you must be hired by an employer. Apprenticeship employers are formally approved by SOLAS in advance of employing apprentices. Apprentices get a formal contract of employment as part of their apprenticeship.
Opportunities for this apprenticeship arise on an ongoing basis throughout the year. To secure an apprenticeship contract of employment, you should target companies you are interested in and apply to them directly.
To find an apprenticeship, you can search apprenticeship vacancies and a list of currently approved apprentice employers on the Apprenticeship Jobs & Employers Portal . You can search for vacancies by location, and employers in each apprenticeship.
Use this link to explore a list of Approved Employers by Region and by Apprenticeship type.
Full eligibility criteria for this apprenticeship are available in the Electrical Instrumentation Apprenticeship brochure .
Colour vision requirements
Electrical Instrumentation Apprenticeship applicants are required to pass a colour vision test approved by SOLAS.
Finding an Employer
Finding an employer or registering your interest with an official Coordinating Provider is one of the first things you need to do to start an apprenticeship.
To find an apprenticeship and secure an apprenticeship work contract you can search apprenticeship vacancies on the Apprenticeship Jobs Portal . You can search for vacancies by location and by apprenticeship type.
Your local Education and Training Board may also hold details of employers seeking to employ an apprentice.
You should also directly connect with local employers who might be interested in taking on an apprentice. It is a great idea to get a part time job with a local employer who might be more inclined to take you on as an apprentice following a successful work experience placement or a part time job contract.
Further information about this apprenticeship may be available from the following organisations on this website:
Organisations supporting this apprenticeship
Where we know of supporting organisations we list these below:
Online Job Sites
Here are some direct links to employment websites that frequently list apprenticeship vacancies.
Note: These websites may include vacancies that are not QQI accredited Apprenticeships.
Pay & Fees
Employment Salary (On-the-job)
The employer pays you a salary while you are being trained on-the-job. The rate of pay is agreed between you and your employer.
Training Allowance (Off-the-job)
A training allowance is paid by the local Education and Training Board (ETB) while you are attending the off-the-job training. In some cases, a contribution towards travel or accommodation costs may be paid.
The sector the apprentice's employer is engaged in will determine the allowance payable. These allowances are calculated on the gross wages paid by industry in each sector. The weekly gross wage norms in electrical contracting are listed below.

View more details on rates of pay at Connect Trade Union.
(Connect is the largest trade union representing construction, electrical, and technical workers in Ireland.)
View rates of pay for other industries here.
View Information on taxation for off-the-job payments here.
For information on how to access payslips via PEOPLEXD, see out the Apprentice Payee PeopleXD for Payees User Reference Guide .
FEES
Apprentices complete two of their three phases of off-the-job training in a higher education institution. A student contribution must be paid for this part of the training.
The amount of the student contribution is a proportion of the annual student contribution paid by students who are attending a full-time course in higher education. The student contribution is paid directly to the higher education institution.
The student contribution for this apprenticeship is €1,719 for Phase 4 and €1,000 for Phase 6.

















